- sales@completestudweld.com
- 216-904-4008
ARC Stud Welding -Threaded & No Thread Weld Studs – Technical Details
Threaded & No Thread Weld Studs: Complete Stud Welding has various types of externally and
internally threaded weld studs and No Thread weld studs. These weld studs are used in many
industrial and construction applications.
Specifications: Complete Stud Welding studs are commonly produced to AWS Specifications D1.1,
D1.5 and or D1.6. Threaded weld studs and No Thread weld studs are available upon request to
various international specifications. Should Certifications be required, please request these as part of
the quotation details and at the time of order.
Threads: The chart below depicts the thread standards for imperial and metric external and internal
threads. Unless requested or quoted otherwise, threads will be quoted based on these common
thread standards.
Unless indicated or quoted otherwise, external threads will be a rolled type thread. The strength and
surface finish of rolled threads are considered to be superior to cut type threads.
Flux: All Standard Arc Welding Studs are flux loaded for diameters greater than 3/16”.
Length: The length dimension (L) indicated throughout these specifications is the overall length of
the stud Before Weld (BW). The After Weld (AW) length will be shorter based on the stud diameter as
depicted in the chart below:
Material: Low Carbon Steel weld studs are available in ASTM A108 / A29, Grade C1010 to C1020
material per AWS D1.1. In Stainless Steel, ASTM A-276 / A-493 Grades 302, 304, 310, 316, 321 are
options. Stainless threaded weld studs are mostly stocked in grade 302HQ / 30430.
Plating: All CSW ARC Weld Studs are supplied with a plain finish / unplated condition. Upon request,
CSW can provide Zinc Plating, Nickel Plating and Copper Plating. Zinc plated studs must be capped
on the weld end to preclude the plating from compromising the weld quality.
Annealing: Standard in stock product is not post annealed. Low carbon steel and stainless steel
studs can be annealed to a maximum of 75 Rockwell B hardness and 85 Rockwell B hardness,
respectively.
Ferrules: The standard ferrule shipped for each thread diameter is listed on the specification page
for each type of threaded weld stud. If other ferrules are desired, please specify at time of order. For
other ferrule options please see General Ferrule Specification or contact your CSW representative for
assistance.
Accessories: For required accessories, please see each specification page or contact your CSW
representative for assistance.
Tensile and Torque Strengths: The 2 charts – Standard ARC Welding Studs – Tensile / Torque Strengths can be found under ARC Stud Welding – General Information.
The data was calculated based on the formulas shown below.
*META is used instead of root area in calculating screw strengths because of closer correlation with
actual tensile strength. META is based on mean diameter, which is the diameter of an imaginary
coaxial cylinder whose surface would pass through the thread profile approximately midway
between the minor and pitch diameters.
**Please note, in actual practice a stud should not be used at its yield load. A factor of safety must
be applied. It is generally recommended that studs be used at no more than 60% of yield. However
the factor of safety may vary up or down, depending on the application. The user will determine the
appropriate safety factor.
***Please note, Torque figures based on assumption that excessive deformation of thread has not
taken relationship between torque/tension out of its proportional range. All torque figures are shown
in foot pounds (ft lbs).
Shear values were calculated at 75% of the Ultimate Tensile Load of the stud.
CD Weld Studs – Technical Details
Threaded & No Thread CD Weld Studs: Complete Stud Welding has various sizes of externally and
internally threaded weld studs and various shapes and size of no thread weld studs. These weld studs
are used in various construction, automotive and industrial applications.
Threads: The chart below depicts the thread standards for imperial and metric external and internal
threads. Unless requested or quoted otherwise, threads will be quoted based on these common
thread standards.
Unless indicated or quoted otherwise, external threads will be a rolled type thread. The strength and
surface finish of rolled threads are considered to be superior to cut type threads.
Auto Feed Quality:
All CD weld studs are available in auto feed quality. This allows for usage in auto
feed stud welding systems. Auto feed hand guns and weld heads are available with the power
source(s) and feeding equipment for incorporation into automated CNC and robotic systems.
Auto feed quality should be requested at the time of quotation.
Material: The chart below depicts the common material types with corresponding typical tensile
strengths used to produce CD Weld Studs.
Plating: For mild steel studs, copper plating is standard for externally threaded studs.
Upon request Nickel, Zinc and other plating’s are available.
Annealing: All low carbon steel and stainless steel studs are annealed where required.
Weld Base: CD Studs are available in the Flanged, Small-Flanged and Non-Flanged condition.
Length Reduction: CD Studs have no appreciable length reduction after welding.
Shielding: The CD Process does not utilize ferrules or arc shields as with the ARC Stud
Welding Process.
Generally shielding gas is not required.
Welding Position: CD Studs can easily be welded in the down hand, side hand and
overhead positions.
CD Stud Welding Guidelines
The following guidelines should be followed for producing and maintaining good CD Stud Welds:
•Ensure the stud welding equipment is capable of welding the stud size intended to be welded.
• Ensure the Stud Welding Equipment is in proper working order and that all cable and ground
connections are tight.
• Weld surface cleanliness. The surface should be free from excessive oils, grease and other lubricants
and from rust, mill scale, and other oxides. These conditions contribute to high electrical resistance
in areas of welding and grounding.
• Weld surface imperfections, such as extreme roughness, which can prevent complete fusion in the
weld area and or interfere with the time duration of the process, should be avoided.
• The stud axis must be perpendicular to the work surface to obtain complete fusion.
• Proper weld end design of the stud is necessary. The tip size, weld base diameter and face angle
must be correct for the application.
• The operator should follow the equipment manufacturer’s setup parameters (i.e.. Weld voltage,
Spring pressure, Plunge and when using GAP or Drawn Arc Method, Lift).
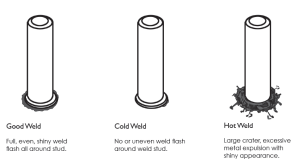
• Visually inspect all welds for 360 degree weld flash. See next page for illustrations of Good, Cold
and Hot welds. If a questionable weld is evident after the welds have been visually inspected, the
weld should be mechanically tested.
• Mechanically test 2 welded studs at the start of each shift and change in stud size.
• Mechanical Testing of CD stud welds should be done by bend testing or torque testing.
The tests are used to establish welding conditions and qualify production studs. The stud and or
weld may be tensile tested and or submitted to other forms of destructive or non-destructive testing
as the application requires.
• The bend test should be performed by bending the stud 30 degrees by striking with a hammer or,
preferably, bending with a pipe.
• Torque values are given in the subsequent table for various stud materials
and stud diameters.
CD Stud Weld Inspection – Visual
Short Cycle Weld Studs – Technical Details
Threaded & No Thread Short Cycle (SC) Weld Studs: Complete Stud Welding has various sizes of
externally and internally threaded weld studs and various sizes of no thread weld studs. These
weld studs are used in various automotive and industrial applications.
Threads: The chart below depicts the thread standards for imperial and metric external and
internal threads. Unless requested or quoted otherwise, threads will be quoted based on these
common thread standards.
Unless indicated or quoted otherwise, external threads will be a rolled type thread. The strength
and surface finish of rolled threads are considered to be superior to cut type threads.
Auto Feed Quality: All SC weld studs are available in auto feed quality. This allows for usage in
auto feed stud welding systems. Auto feed hand guns and weld heads are available with the
power source(s) and feeding equipment for incorporation into automated CNC and robotic
systems. Auto feed quality should be requested at the time of quotation.
Material: The chart below depicts the common material types with corresponding typical
tensile strengths used to produce SC Weld Studs.
Plating: For mild steel studs, copper plating is standard for externally threaded studs.
Upon request Nickel, Zinc and other plating’s are available.
Annealing: All low carbon steel and stainless steel studs are annealed where required.
Weld Base: Studs are available in the Flanged condition. Other flange diameters and
weld base dimensions are quoted upon request.
Length Reduction: SC Studs have an approximate length reduction from welding of
0.030 inches.
Flux: SC Studs are not flux loaded.
Shielding: The SC Process does not require shielding gas up through 1/4” diameter studs,
however, in most cases it is recommended to use a shielding gas.
Welding Position: SC Studs can be welded in the down hand, side hand and overhead
positions. In the side hand and overhead positions this becomes increasingly more difficult
as the stud diameter increases.
Available Sizes: SC studs are available in diameters up through 1/2” (M12) and length is
not a limitation. SC studs over 3/8” Diameter typically do not have a flange and are made
to order.
Visual Inspection: The weld is acceptable if a 360 degree weld flash is present.
Mechanical Testing: Testing can be done by bend testing or torque testing.
The bend test should be done by bending the stud 30 degrees by striking with a hammer
or bending with a pipe.
For torque testing, please refer to the CD Stud Weld Inspection – Mechanical
(torque values). These values are the same for SC type studs.
Weight Charts: Please see the CD Weld Stud Weight Charts for these values.