Robotic stud welding is the automated manufacturing process where a robotic arm or CNC-controlled computers, instead of a human operator, is used to precisely position and weld studs on metals.
It combines the principles of a computer and stud welding, where a metal fastener is welded to a base metal using an electric arc.
A robotic arm moves the stud welding head to pre-programmed locations, automatically feeds a weld stud and welds the stud in milli-seconds. A computer assisted stud welder can weld in a 1.5-second cycle time per stud, including robotic motion.
This process significantly increases the speed, accuracy, and consistency of repetitive welding tasks, allowing for 24-hour operation and making it ideal for large-scale production in industries like automotive, shipbuilding, and construction.
Robots can easily weld studs to complex 3D components, thanks to their multi-axis movement capabilities.
Advantages of Automated Robotic / CNS Stud Welding
Superior Quality, Precision & Repeatability: Exact stud placement every time, this consistency ensures precise and reliable placement, critical in automotive and aerospace. Eliminates human error and ensures uniform weld penetration.
High Precision: For intricate 3D components or tight-tolerance applications, a robot’s ability to position the stud welding head with pinpoint accuracy is a major advantage.
Increased Productivity: Automated production can operate continuously, 24/7, leading to higher throughput and reduced labor costs.
Quality Control: Some systems include sensors or vision systems to confirm weld integrity and placement.
Versatility: This process is highly adaptable for a wide range of applications and easily integrated into existing automated production lines.
Labor Savings: Robots can weld hundreds of studs per hour.
Improved Safety: Automating the welding process removes humans from the direct welding operation, keeping employees safe from accidents.
Single-Sided Access: Stud welding only requires access to one side of the workpiece, which creates a leak-proof connection without holes.
Common Applications
Robotic stud welding is widely used in industries that require high-speed, repetitive fastening of metal parts.
Appliances and HVAC: Mounting components without drilling holes. Used in manufacturing cookware and household appliances
Electrical and Mechanical Equipment: Fastening components in electrical panels, circuit boards, and other machinery.
Automotive: Used for various components in car bodies and electric vehicle assembly.
Sign Installation: A fast method for attaching signs and letters. Weld studs create a hidden fastening system that provides a strong, durable bond for both indoor and outdoor applications. This prevents damage to the sign’s surface and ensuring a strong, permanent connection on metal, stone, brick, and concrete.
Shipbuilding: Securing insulation and electrical wiring to bulkheads and decks.
Aerospace: Lightweight structural fastening where precision is critical.
Construction: Welding shear connectors and anchors to steel beams for composite construction. Applied in industrial buildings and bridge decks.
Capacitor Discharge (CD) Stud Welding & Arc Stud Welding
Capacitor Discharge (CD) stud welding is used for thin-gauge materials and small-diameter studs with minimal burn-through, warping, or marking on the base reverse side.
Arc stud welding is used to weld large diameter fasteners to rougher and thicker base metals.
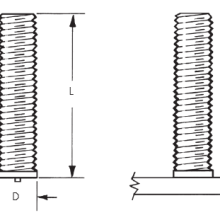
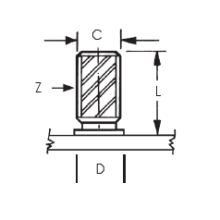
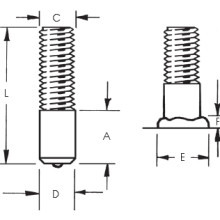
Weld Studs
Full-threaded and partial-thread weld studs offer flexibility in assembling components, providing a sturdy, permanent base for attaching additional components.
Custom designed weld studs are available.
Questions?
Complete Stud Welding can supply expert guidance.



Comments are closed.