Securing insulation might seem like a minor detail in a large construction or industrial project. However, the integrity of your thermal barrier depends almost entirely on the fasteners or Insulation pins you choose. Might be small, but these pins play a big role in how well insulation stays in place. If the insulation sags or falls, your energy efficiency vanishes.
Whether you are working on HVAC ducts, boilers, ovens, tanks, or industrial insulation, choosing the right insulation pins makes a big difference in performance and durability. Complete Stud Welding brings a comprehensive guide that goes deep, but remains straightforward. You will walk away knowing what insulation pins are, how they work, and which ones fit your project.
What Are Insulation Pins?

Insulation pins are fasteners used to secure insulation materials to metal surfaces. These pins stick out from a surface once welded or fixed. Then the insulation is impaled on the pin. A self-locking washer is added to hold the insulation tight. This method creates a secure hold for materials like blanket insulation, boards, and fiber wool.
Pins can be welded or used with self-adhesive methods, but for industrial metal applications, welding is the most dependable solution.
The goal is a permanent bond. According to data from the North American Insulation Manufacturers Association (NAIMA), properly installed and secured insulation can reduce energy loss in industrial piping and equipment by as much as 20%. Using the wrong insulator pin can lead to “thermal bridging” or complete fastening failure.
How Do They Work?
- A pin is welded or attached to metal.
- The insulation material is pushed over the pin.
- A washer or clip locks the insulation in place.
This holds insulation where screws or adhesives may fail under heat, vibration, or moisture.
The Market is Growing, and Fast
The HVAC insulation market tells an important story. The global market reached $6.53 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit $9.28 billion by 2030, growing at 4.7% annually. This growth reflects real demand across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. As energy efficiency becomes non-negotiable, more projects require proper insulation installation—and that means more need for reliable fastening solutions.
In North America alone, the HVAC insulation market captured 35.1% of the global market share in 2024. Construction activity continues to climb, driven by stricter building codes and pressure to reduce energy consumption. For contractors and engineers, this means working faster and smarter. Choosing the right insulation pins directly impacts both speed and quality.
Types of Insulation Fasteners
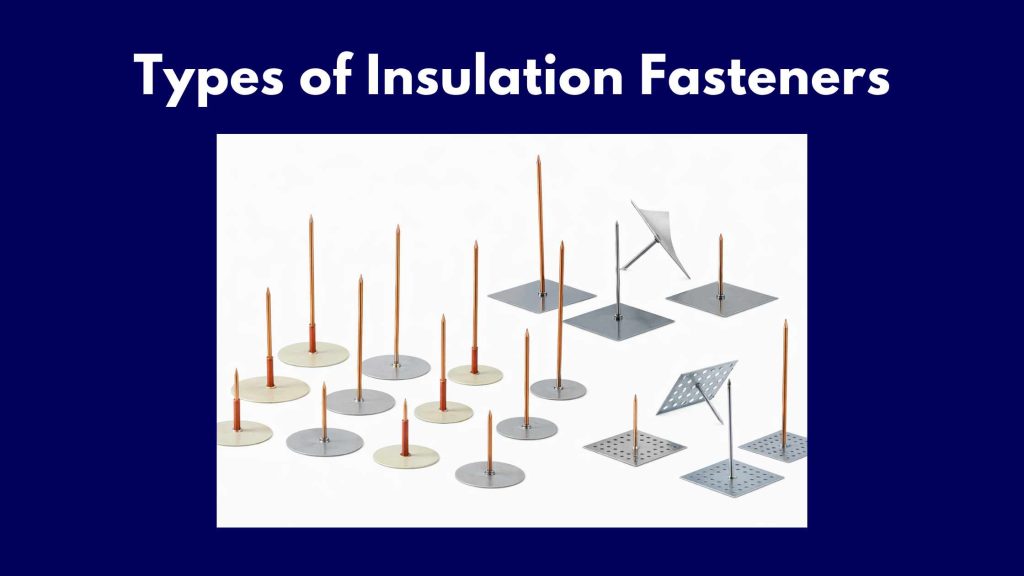
Not every project allows for welding, and not every surface is suited for adhesives. Our experts generally categorize these into two main groups.
CD Weld Pins
CD weld pins stand for capacitor discharge weld pins. These work with CD welding equipment and offer several advantages. They install quickly and work on rusty, painted, or mill-scaled surfaces without requiring preparation. Most contractors prefer these because the equipment delivers consistent results with minimal training required.
CD pins typically come in 10-gauge or 12-gauge diameters. The smaller sizes, like .105″ or .135″ diameter, handle thin-gauge duct walls effectively. Cycle speeds reach 40 studs per minute on modern equipment, making them ideal when time matters.
Double-Pointed Insulation Pins
Double-pointed pins work with arc welding equipment. These pins have points on both ends, which helps them penetrate insulation material cleanly. Arc pins typically deliver a tensile strength of 60,000 psi minimum and yield of 50,000 psi minimum when welded to low-carbon steel.
The downside? Arc welding takes longer than CD methods and requires more operator skill. But for thick insulation or demanding applications, arc pins often provide superior holding power.
Insulation Stick Pins
If you cannot weld due to safety hazards or thin substrates, stick pins insulation is the go-to alternative. These feature a perforated or solid base with a high-strength adhesive. You simply peel the backing and press the insulator pins onto a clean surface.
While stick pins for insulation are easier to install for DIY or light commercial work, they rely heavily on the quality of the adhesive and the cleanliness of the metal.
Cup Head Weld Pins
Cup head pins feature a cupped surface that sits flush against the outside of your insulation. These work especially well with pre-insulated duct systems and ship hull insulation. The cup head distributes force over a larger surface area, preventing the pin from pulling through the insulation material.
These pins come in various sizes depending on your base metal thickness and the insulation weight. Thicker applications demand larger washers and longer pins.
Self-Locking Washers and Speed Clips
Sometimes you need a mechanical fastening solution instead of welding. Self-locking washers hold insulation without melting or fusing anything. Speed clips work similarly, offering quick installation when you’re working with pre-assembled systems or can’t access welding equipment.
Technical Options for Insulation Pins

There are several types of insulation pins. Choosing one depends on project needs.
| Type | Description | Best For |
| Weldable Insulation Pins | Pins welded to metal using stud welding | Heavy insulation, industrial use |
| CD Weld Pins | Pins for capacitor discharge welding | Thin gauge metal, fast installation |
| Double Pointed Weld Pins | Pins for arc stud welding applications | Standard insulation jobs |
| Self-Adhesive Pins | Adhesive pins for non-weld surfaces | Light insulation, DIY |
| Stick Pins | Simple pins hammered into place | Temporary fixes or light loads |
Common Uses of Insulation Pins

Insulation pins are used across many industries. Here are typical use areas:
- HVAC ducts and sheet metal
- Industrial ovens and furnaces
- Boiler walls and tanks
- Hot and cold process equipment
- Acoustic and thermal insulation systems
A good insulation attachment reduces energy loss and lowers operating costs. In commercial buildings, proper insulation can cut energy use by about 20 to 30 percent compared to poorly installed insulation. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, effective insulation keeps indoor temperatures steady and saves energy.
Crucial Factors To Keep In Mind When Choosing Your Pins

1. Base Material
The metal you’re fastening to determines which pins work best. If you’re installing insulation on galvanized steel ductwork, use galvanized pins to prevent bimetallic corrosion. The same principle applies to stainless steel systems—match your pin material to your base metal.
For boiler walls made from high-temperature steels like 16Mo3, you need pins manufactured from compatible materials. Using mismatched metals invites premature failure from galvanic corrosion or thermal expansion differences.
2. Base Metal Thickness and Pin Diameter Ratio
Metallurgists have established clear guidelines here. When the ratio between stud diameter and base material thickness is lower than 1:2, the base material will deform. When that ratio is higher than 1:2, the stud itself will fail. This isn’t theoretical—it comes from decades of industrial experience.
For example, a .135″ diameter pin on thin sheet metal needs careful selection. Go too small, and the metal warps. Go too large, and the pin snaps. The middle ground exists, but finding it requires knowing your base metal thickness precisely.
3. Temperature Range
Insulation pins operate in environments ranging from cold storage rooms to boiler walls exceeding 1,000°C. Standard carbon steel pins work fine for moderate temperatures. High-temperature applications demand pins from materials like copper-coated steel or specialized alloys.
Your insulation material temperature rating drives this choice. If your application sees regular exposure above 600°C, base your pin selection on that requirement, not on cheaper alternatives.
4. Welding Equipment You’re Using
Not every pin works with every welder. CD equipment and arc equipment have different power profiles and heat characteristics. Using the wrong pin type for your equipment means:
- Weak, inconsistent welds
- Burned or damaged insulation
- Wasted time resetting and reworking connections
Always verify your equipment’s capabilities before ordering pins. A 12-gauge arc pin won’t work reliably on a capacitor discharge unit designed for 10-gauge CD pins.
5. Insulation Type
Soft blanket insulation and board insulation behave differently. Firmer insulation needs longer pins. Lightweight materials do not.
6. PIN Length and Diameter
Pins come in sizes. The length must surpass the insulation thickness. The diameter must be strong enough to support the load. A mismatch can lead to sagging or failure.
7. Washer or Clip Selection
Self-locking washers grip the pin once insulation is installed. The right washer prevents insulation from sliding off over time.
Key Differences: CD Pins vs Arc Pins vs Speed Clips

| Feature | CD Weld Pins | Arc Weld Pins | Speed Clips |
| Installation Speed | 3-40 per minute | 1-5 per minute | Immediate mechanical |
| Surface Prep Required | Minimal | Requires cleaning | None |
| Tensile Strength | 50,000-60,000 psi | 60,000+ psi | Variable |
| Equipment Cost | Moderate | Lower | Minimal |
| Learning Curve | Easy | Moderate to steep | Very easy |
| Best For | HVAC ducts, quick work | Thick materials, high strength | Temporary or mechanical systems |
| Environmental Factors | Works in paint/rust | Needs clean surface | Works anywhere |
The Installation Process Matters
You have the right pins. Now what? Installation quality determines whether your insulation stays put for years or fails in months.
Stud welding integrates the same rules as other arc welding methods. The electric arc melts the end of the pin and the base material surface. The pin then pushes into the melted pool automatically, creating a fusion weld. This process demands trained, experienced operators.
Anyone performing stud welding work should be certified and trained. Different welding methods require proper certification. Rushing this step leads to poor weld quality and expensive rework.
When installing CD pins, allow the capacitors to fully charge before each weld. On arc systems, strike the arc cleanly and maintain consistent arc length. These fundamentals sound simple, but make the difference between professional results and failed installations.
How to Select the Right Pin for Your Project

Work through this checklist before making your purchase decision.
Step 1: Determine Base Metal Type and Thickness
Identify whether you’re fastening to steel, stainless, aluminum, or painted/galvanized surfaces. Measure thickness precisely.
Step 2: Identify Your Welding Equipment
Do you have CD equipment or arc welding capability? Match the pin type to the equipment.
Step 3: Consider Your Insulation Material and Weight
Heavier insulation needs larger washers and longer pins. Lightweight fiberglass differs from dense acoustic board.
Step 4: Check Temperature Range
What temperatures will these pins experience? Standard pins, high-temp alloys, or specialty materials?
Step 5: Calculate Installation Speed Requirements
How many pins do you need to install per day? CD pins excel when speed matters. Arc pins work fine for smaller quantities.
Step 6: Confirm Surface Conditions
Will surfaces be clean, rusty, or painted? CD pins handle dirty surfaces. Arc methods need cleaner surfaces.
Step 7: Verify Torque and Strength Ratings
Reference the technical specifications table from your equipment supplier. Ensure your pin diameter and material match the torque requirements.
Why Pick Complete Stud Welding?
We focus on real solutions. We don’t just sell pins. We help you match the pin to your job. Our team looks at material, thickness, environment, and performance needs before we recommend pins.
If you want custom help, call 216-904-4008. We can walk you through specifications and fit. We want your project to succeed.
Final Thoughts
Insulation pins seem like small components in large projects. But small details compound into major outcomes. The right pin selection ensures your insulation holds securely, your installation moves quickly, and your results last. The wrong choice creates delays, rework, and premature failure.
Understanding your options—CD pins, arc pins, double-pointed pins, cup head pins, and mechanical alternatives—helps you make informed decisions. Knowing how material compatibility, temperature ratings, base metal thickness, and equipment capabilities intersect prevents expensive mistakes.
Your next insulation project should run smoothly. Start by choosing the right pins. Complete Stud Welding stands ready to help you find them.




Comments are closed.